skpro package¶
Subpackages¶
Submodules¶
skpro.base module¶
-
class
skpro.base.BayesianVendorEstimator(model=None, adapter=None)[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.VendorEstimatorVendor estimator for Bayesian methods
ProbabilisticEstimator that interfaces a Bayesian vendor using a BayesianVendorInterface and and sample-based Adapter.
-
class
Distribution(estimator, X, selection=slice(None, None, None), mode='elementwise')[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.Distribution-
X¶ Reference of the test features that are ought to correspond with the predictive distribution represented by the interface.
The interface methods (e.g. pdf) can use X to construct and exhibit the predictive distribution properties of the interface (e.g. construct the predicted pdf based on X)
Note that X automatically reflects the feature point for which the interface is ought to represent the distributional prediction. For given M x n features, X will thus represent an 1 x n vector that provides the bases for the predicted distribution. However, if the
vectorvalued()decorator is applied X will represent the full M x n matrix for an efficient vectorized implementation.Getter: Returns the test features based on the current subset selection Setter: Sets the data reference Type: array
-
lp2¶
-
mean(*args, **kwargs)¶ Mean prediction
Returns: Return type: The mean prediction that corresponds to self.X
-
ppf(q, *args, **kwargs)¶ Percent point function (inverse of cdf — percentiles).
Parameters: q – Returns: Return type: float
-
replicate(selection=None, mode=None)¶ Replicates the distribution object
Parameters: - selection (None | slice | int (optional)) – Subset point selection of the distribution copy
- mode (str (optional)) – Interface mode (‘elementwise’ or ‘batch’)
Returns: Return type: skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution
-
-
class
ImplementsEnhancedInterface(name, bases, clsdict)¶ Bases:
abc.ABCMetaMeta-class for distribution interface
Enhances the distribution interface behind the scenes with automatic caching and syntactic sugar for element-wise access of the distributions
-
mro() → list¶ return a type’s method resolution order
-
register(subclass)¶ Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
-
-
fit(X, y)¶ Fits the vendor model
Parameters: - X (numpy array or sparse matrix of shape [n_samples,n_features]) – Training data
- y (numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_targets]) – Target values. Will be cast to X’s dtype if necessary
Returns: self
Return type: returns an instance of self.
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
name()¶
-
predict(X)¶ Predicts using the vendor model
Parameters: X ({array-like, sparse matrix}, shape = (n_samples, n_features)) – Samples. Returns: Returns predicted distributions Return type: Distributioninterface representing n_samples predictions
-
score(X, y, sample=True, return_std=False)¶ Returns the log-loss score
Parameters: - X (np.array) – Features
- y (np.array) – Labels
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Log-loss score
Return type: mixed
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
class
-
class
skpro.base.BayesianVendorInterface[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.VendorInterfaceAbstract base class for a Bayesian vendor
Notes
Must implement the samples method that returns Bayesian posterior samples. The sample method should be cached using the
functools.lru_cachedecorator to increase performance-
on_fit(X, y)¶ Implements vendor fit procedure
Parameters: - X (np.array) – Training features
- y (np.array) – Training labels
Returns: Return type:
-
-
class
skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator[source]¶ Bases:
sklearn.base.BaseEstimatorAbstract base class for probabilistic prediction models
Notes
All probabilistic estimators should specify all the parameters that can be set at the class level in their
__init__as explicit keyword arguments (no*argsor**kwargs).-
class
Distribution(estimator, X, selection=slice(None, None, None), mode='elementwise')[source]¶ Bases:
objectAbstract base class for the distribution interface returned by probabilistic estimators
Parameters: - estimator (
skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator) – Parent probabilistic estimator object - X (np.array) – Features
- selection (slice | int (optional)) – Subset point selection of the features
- mode (str) – Interface mode (‘elementwise’ or ‘batch’)
-
X¶ Reference of the test features that are ought to correspond with the predictive distribution represented by the interface.
The interface methods (e.g. pdf) can use X to construct and exhibit the predictive distribution properties of the interface (e.g. construct the predicted pdf based on X)
Note that X automatically reflects the feature point for which the interface is ought to represent the distributional prediction. For given M x n features, X will thus represent an 1 x n vector that provides the bases for the predicted distribution. However, if the
vectorvalued()decorator is applied X will represent the full M x n matrix for an efficient vectorized implementation.Getter: Returns the test features based on the current subset selection Setter: Sets the data reference Type: array
-
mean(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Mean prediction
Returns: Return type: The mean prediction that corresponds to self.X
-
ppf(q, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Percent point function (inverse of cdf — percentiles).
Parameters: q – Returns: Return type: float
-
replicate(selection=None, mode=None)[source]¶ Replicates the distribution object
Parameters: - selection (None | slice | int (optional)) – Subset point selection of the distribution copy
- mode (str (optional)) – Interface mode (‘elementwise’ or ‘batch’)
Returns: Return type: skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution
- estimator (
-
class
ImplementsEnhancedInterface(name, bases, clsdict)[source]¶ Bases:
abc.ABCMetaMeta-class for distribution interface
Enhances the distribution interface behind the scenes with automatic caching and syntactic sugar for element-wise access of the distributions
-
mro() → list¶ return a type’s method resolution order
-
register(subclass)¶ Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
-
-
fit(X, y)[source]¶ Fits the model
Parameters: - X (numpy array or sparse matrix of shape [n_samples,n_features]) – Training data
- y (numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_targets]) – Target values. Will be cast to X’s dtype if necessary
Returns: self
Return type: returns an instance of self.
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
predict(X)[source]¶ Predicts using the model
Parameters: X ({array-like, sparse matrix}, shape = (n_samples, n_features)) – Samples. Returns: Returns predicted distributions Return type: Distributioninterface representing n_samples predictions
-
score(X, y, sample=True, return_std=False)[source]¶ Returns the log-loss score
Parameters: - X (np.array) – Features
- y (np.array) – Labels
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Log-loss score
Return type: mixed
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
class
-
class
skpro.base.VendorEstimator(model=None, adapter=None)[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimatorProbabilisticEstimator that interfaces a vendor using a VendorInterface and Adapter.
Parameters: - model (skpro.base.VendorInterface) – Vendor interface
- adapter (skpro.density.DensityAdapter) – Density adapter
-
class
Distribution(estimator, X, selection=slice(None, None, None), mode='elementwise')[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.Distribution-
X¶ Reference of the test features that are ought to correspond with the predictive distribution represented by the interface.
The interface methods (e.g. pdf) can use X to construct and exhibit the predictive distribution properties of the interface (e.g. construct the predicted pdf based on X)
Note that X automatically reflects the feature point for which the interface is ought to represent the distributional prediction. For given M x n features, X will thus represent an 1 x n vector that provides the bases for the predicted distribution. However, if the
vectorvalued()decorator is applied X will represent the full M x n matrix for an efficient vectorized implementation.Getter: Returns the test features based on the current subset selection Setter: Sets the data reference Type: array
-
cdf(x, *args, **kwargs)¶
-
lp2¶
-
mean(*args, **kwargs)¶ Mean prediction
Returns: Return type: The mean prediction that corresponds to self.X
-
pdf(x, *args, **kwargs)¶
-
point¶
-
ppf(q, *args, **kwargs)¶ Percent point function (inverse of cdf — percentiles).
Parameters: q – Returns: Return type: float
-
replicate(selection=None, mode=None)¶ Replicates the distribution object
Parameters: - selection (None | slice | int (optional)) – Subset point selection of the distribution copy
- mode (str (optional)) – Interface mode (‘elementwise’ or ‘batch’)
Returns: Return type: skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution
-
std¶
-
-
class
ImplementsEnhancedInterface(name, bases, clsdict)¶ Bases:
abc.ABCMetaMeta-class for distribution interface
Enhances the distribution interface behind the scenes with automatic caching and syntactic sugar for element-wise access of the distributions
-
mro() → list¶ return a type’s method resolution order
-
register(subclass)¶ Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
-
-
fit(X, y)[source]¶ Fits the vendor model
Parameters: - X (numpy array or sparse matrix of shape [n_samples,n_features]) – Training data
- y (numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_targets]) – Target values. Will be cast to X’s dtype if necessary
Returns: self
Return type: returns an instance of self.
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
name()¶
-
predict(X)[source]¶ Predicts using the vendor model
Parameters: X ({array-like, sparse matrix}, shape = (n_samples, n_features)) – Samples. Returns: Returns predicted distributions Return type: Distributioninterface representing n_samples predictions
-
score(X, y, sample=True, return_std=False)¶ Returns the log-loss score
Parameters: - X (np.array) – Features
- y (np.array) – Labels
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Log-loss score
Return type: mixed
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
skpro.density module¶
-
class
skpro.density.DensityAdapter[source]¶ Bases:
sklearn.base.BaseEstimatorAbtract base class for density adapter that transform an input into an density cdf/pdf interface
-
cdf(x)[source]¶ Cumulative density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Cumulative density function evaluated at x
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
pdf(x)[source]¶ Probability density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Density function evaluated at x
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
-
class
skpro.density.EmpiricalDensityAdapter[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.density.DensityAdapterDensityAdapter that uses empirical cdf to transform samples
-
cdf(x)[source]¶ Cumulative density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Cumulative density function evaluated at x
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
pdf(x)[source]¶ Probability density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Density function evaluated at x
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
-
class
skpro.density.KernelDensityAdapter(estimator=KernelDensity(algorithm='auto', atol=0, bandwidth=1.0, breadth_first=True, kernel='gaussian', leaf_size=40, metric='euclidean', metric_params=None, rtol=0))[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.density.DensityAdapterDensityAdapter that uses kernel density estimation to transform samples
-
cdf(x)[source]¶ Cumulative density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Cumulative density function evaluated at x
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
pdf(x)[source]¶ Probability density function
Parameters: x – Returns: Return type: mixed Density function evaluated at x
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
skpro.ensemble module¶
-
class
skpro.ensemble.BaggingRegressor(base_estimator=None, n_estimators=10, max_samples=1.0, max_features=1.0, bootstrap=True, bootstrap_features=False, oob_score=False, warm_start=False, n_jobs=None, random_state=None, verbose=0)[source]¶ Bases:
sklearn.ensemble.bagging.BaggingRegressor,skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator-
class
Distribution(estimator, X, distributions, n_estimators)[source]¶ Bases:
skpro.base.Distribution-
X¶ Reference of the test features that are ought to correspond with the predictive distribution represented by the interface.
The interface methods (e.g. pdf) can use X to construct and exhibit the predictive distribution properties of the interface (e.g. construct the predicted pdf based on X)
Note that X automatically reflects the feature point for which the interface is ought to represent the distributional prediction. For given M x n features, X will thus represent an 1 x n vector that provides the bases for the predicted distribution. However, if the
vectorvalued()decorator is applied X will represent the full M x n matrix for an efficient vectorized implementation.Getter: Returns the test features based on the current subset selection Setter: Sets the data reference Type: array
-
cdf(x, *args, **kwargs)¶
-
lp2¶
-
mean(*args, **kwargs)¶ Mean prediction
Returns: Return type: The mean prediction that corresponds to self.X
-
pdf(x, *args, **kwargs)¶
-
point¶
-
ppf(q, *args, **kwargs)¶ Percent point function (inverse of cdf — percentiles).
Parameters: q – Returns: Return type: float
-
replicate(selection=None, mode=None)¶ Replicates the distribution object
Parameters: - selection (None | slice | int (optional)) – Subset point selection of the distribution copy
- mode (str (optional)) – Interface mode (‘elementwise’ or ‘batch’)
Returns: Return type: skpro.base.ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution
-
std¶
-
-
class
ImplementsEnhancedInterface(name, bases, clsdict)¶ Bases:
abc.ABCMetaMeta-class for distribution interface
Enhances the distribution interface behind the scenes with automatic caching and syntactic sugar for element-wise access of the distributions
-
mro() → list¶ return a type’s method resolution order
-
register(subclass)¶ Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
-
-
estimators_samples_¶ The subset of drawn samples for each base estimator.
Returns a dynamically generated list of indices identifying the samples used for fitting each member of the ensemble, i.e., the in-bag samples.
Note: the list is re-created at each call to the property in order to reduce the object memory footprint by not storing the sampling data. Thus fetching the property may be slower than expected.
-
fit(X, y, sample_weight=None)¶ - Build a Bagging ensemble of estimators from the training
- set (X, y).
Parameters: - X ({array-like, sparse matrix} of shape = [n_samples, n_features]) – The training input samples. Sparse matrices are accepted only if they are supported by the base estimator.
- y (array-like, shape = [n_samples]) – The target values (class labels in classification, real numbers in regression).
- sample_weight (array-like, shape = [n_samples] or None) – Sample weights. If None, then samples are equally weighted. Note that this is supported only if the base estimator supports sample weighting.
Returns: self
Return type:
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators. Returns: params – Parameter names mapped to their values. Return type: mapping of string to any
-
name()¶
-
predict(X)[source]¶ Predict regression target for X.
The predicted regression target of an input sample is computed as the averaged predicted distributions of the estimators in the ensemble.
Parameters: X ({array-like, sparse matrix} of shape = [n_samples, n_features]) – The training input samples. Sparse matrices are accepted only if they are supported by the base estimator. Returns: y – The predicted bagged distributions. Return type: skpro.base.Distribution = [n_samples]
-
score(X, y, sample=True, return_std=False)¶ Returns the log-loss score
Parameters: - X (np.array) – Features
- y (np.array) – Labels
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Log-loss score
Return type: mixed
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.Returns: Return type: self
-
class
skpro.metrics module¶
-
skpro.metrics.gneiting_loss(y_true, dist_pred, sample=True, return_std=False)[source]¶ Gneiting loss
Parameters: - y_true (np.array) – The true labels
- dist_pred (ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution) – The predicted distribution
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Loss (with standard deviation if
return_stdis True)Return type: np.array
-
skpro.metrics.linearized_log_loss(y_true, dist_pred, range=1e-10, sample=True, return_std=False)[source]¶ Linearized log loss
Parameters: - y_true (np.array) – The true labels
- dist_pred (ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution) – The predicted distribution
- range (float) – Threshold value of linearization
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Loss (with standard deviation if
return_stdis True)Return type: np.array
-
skpro.metrics.log_loss(y_true, dist_pred, sample=True, return_std=False)[source]¶ Log loss
Parameters: - y_true (np.array) – The true labels
- dist_pred (ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution) – The predicted distribution
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Loss (with standard deviation if
return_stdis True)Return type: np.array
-
skpro.metrics.make_scorer(score_func, greater_is_better=True)[source]¶ Make a scorer from a performance metric or loss function.
This factory function wraps scoring functions for use in GridSearchCV and cross_val_score. It takes a score function, such as
log_loss, and returns a callable that scores an estimator’s output.Parameters: - score_func (callable,) – Score function (or loss function) with signature
score_func(y, y_pred, **kwargs). - greater_is_better (boolean, default=True) – Whether score_func is a score function (default), meaning high is good, or a loss function, meaning low is good. In the latter case, the scorer object will sign-flip the outcome of the score_func.
- **kwargs (additional arguments) – Additional parameters to be passed to score_func.
Returns: scorer – Callable object that returns a scalar score; greater is better.
Return type: callable
- score_func (callable,) – Score function (or loss function) with signature
-
skpro.metrics.rank_probability_loss(y_true, dist_pred, sample=True, return_std=False)[source]¶ Rank probability loss
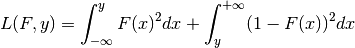
where
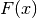 denotes the CDF of the predicted distribution
denotes the CDF of the predicted distributionParameters: - y_true (np.array) – The true labels
- dist_pred (ProbabilisticEstimator.Distribution) – The predicted distribution
- sample (boolean, default=True) – If true, loss will be averaged across the sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Loss (with standard deviation if
return_stdis True)Return type: np.array
-
skpro.metrics.sample_loss(loss, return_std=False)[source]¶ Averages the loss of a sample
Parameters: - loss (np.array) – Loss sample
- return_std (boolean, default=False) – If true, the standard deviation of the loss sample will be returned
Returns: Sample loss (with standard deviation if
return_stdis True)Return type: np.array
skpro.model_selection module¶
-
skpro.model_selection.cross_val_score(estimator, X, y=None, groups=None, scoring=None, cv=None, n_jobs=1, verbose=0, fit_params=None, pre_dispatch='2*n_jobs')[source]¶ Evaluate a score using cross-validation
Parameters: - estimator (estimator object implementing 'fit') – The object to use to fit the data.
- X (array-like) – The data to fit. Can be for example a list, or an array.
- y (array-like, optional, default: None) – The target variable to try to predict in the case of supervised learning.
- groups (array-like, with shape (n_samples,), optional) – Group labels for the samples used while splitting the dataset into train/test set.
- scoring (string, callable or None, optional, default: None) – A string (see model evaluation documentation) or
a scorer callable object / function with signature
scorer(estimator, X, y). - cv (int, cross-validation generator or an iterable, optional) – Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy.
Possible inputs for cv are:
- None, to use the default 3-fold cross validation,
- integer, to specify the number of folds in a (Stratified)KFold,
- An object to be used as a cross-validation generator.
- An iterable yielding train, test splits.
For integer/None inputs, if the estimator is a classifier and
yis either binary or multiclass,StratifiedKFoldis used. In all other cases,KFoldis used. Refer User Guide for the various cross-validation strategies that can be used here. - n_jobs (integer, optional) – The number of CPUs to use to do the computation. -1 means ‘all CPUs’.
- verbose (integer, optional) – The verbosity level.
- fit_params (dict, optional) – Parameters to pass to the fit method of the estimator.
- pre_dispatch (int, or string, optional) –
Controls the number of jobs that get dispatched during parallel execution. Reducing this number can be useful to avoid an explosion of memory consumption when more jobs get dispatched than CPUs can process. This parameter can be:
- None, in which case all the jobs are immediately created and spawned. Use this for lightweight and fast-running jobs, to avoid delays due to on-demand spawning of the jobs
- An int, giving the exact number of total jobs that are spawned
- A string, giving an expression as a function of n_jobs, as in ‘2*n_jobs’
Returns: scores – Array of scores of the estimator for each run of the cross validation with their corresponding uncertainty.
Return type: numpy.array, shape=(len(list(cv)), 2)
See also
skpro.metrics.make_scorer()- Make a scorer from a performance metric or loss function.
skpro.utils module¶
-
skpro.utils.ensure_existence(f)[source]¶ Ensures that method is not marked as non_existent
Parameters: Method (f) – Raises: NotImplementedError if the method is marked as non existent Returns: Return type: Method f